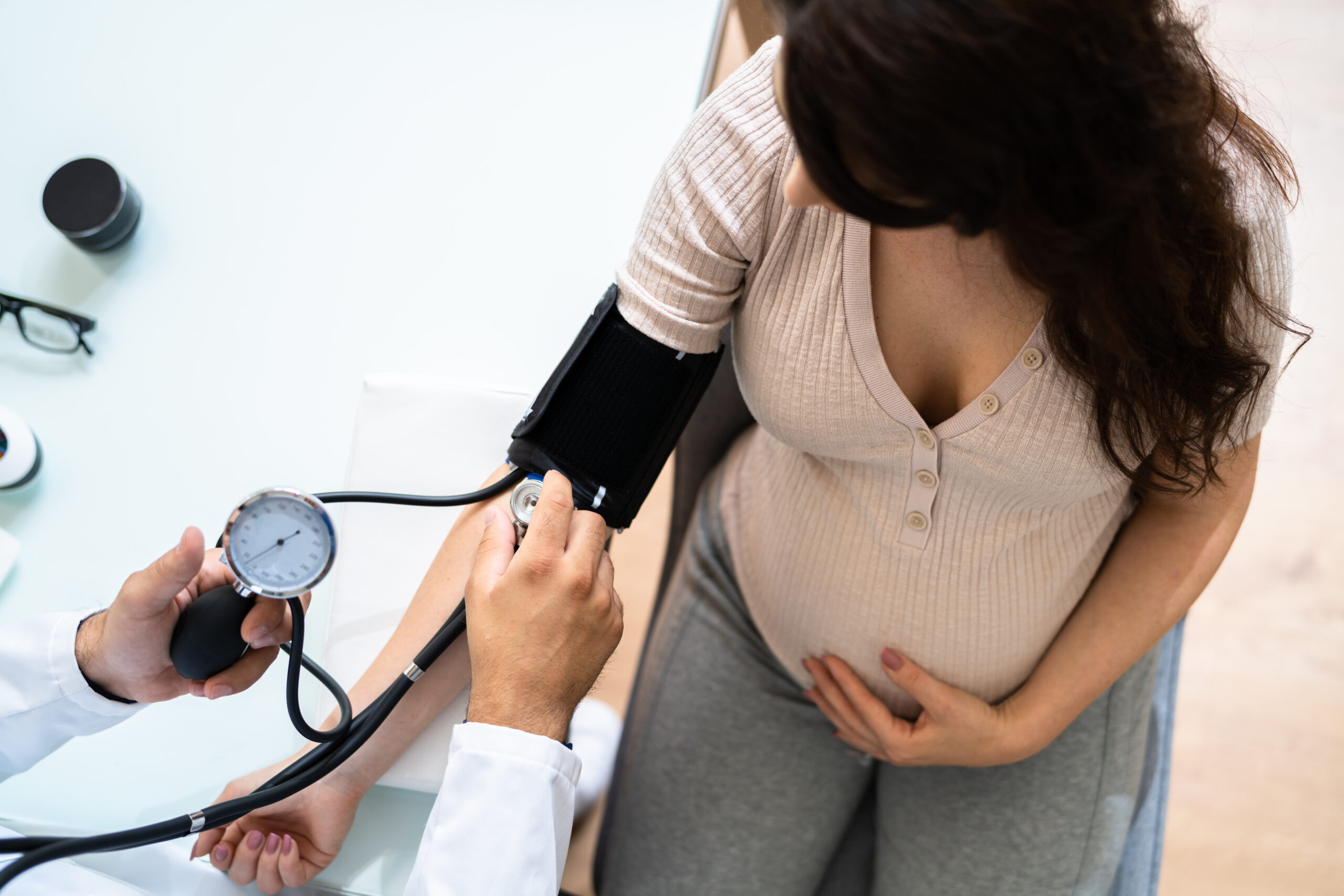
Preeclampsia / high blood pressure
Blood pressure and other regulatory disorders during pregnancy require special attention.
Preeclampsia and high blood pressure are among the most common complications of pregnancy and can have serious consequences for both the expectant mother and the baby.
The disease can manifest during pregnancy or in the postpartum period. With timely diagnosis and treatment, long-term effects and complications can usually be prevented.
Preeclampsia occurs in approximately 41 percent of all pregnancies. Most cases only become apparent after the 34th week of pregnancy; the condition is less common in early pregnancy. There are mild and severe forms. In addition, a variety of accompanying symptoms are possible, depending on the organ system affected. Affected organs include the kidneys, liver, sometimes the brain, lungs, blood clotting system, and placenta.
Typical symptoms of preeclampsia
-
-
- Headache
- dizziness
- Visual disturbances such as eye flickering
- severe lower or upper abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- severe and sudden weight gain (more than one kilogram per week of pregnancy)
- increased water retention (edema) with tight skin
-