Hormonal disorder in women
Hormones in balance – your health in focus
Hormones play a central role in a woman's life, from puberty through pregnancy and breastfeeding to menopause. However, a disruption in the delicate balance of these neurotransmitters can cause a variety of symptoms that can be both physically and emotionally stressful.
Our gynecological practice is dedicated to providing professional support for hormonal challenges such as menstrual irregularities, thyroid problems, or menopausal symptoms. Through targeted diagnostics and individualized treatment concepts, we help you maintain or improve your quality of life. You and your needs are always our primary focus.


Speed disorder
Menstrual disorders, such as irregular cycles, painful bleeding or even the absence of periods, can have a variety of causes and significantly impact quality of life.
There are many possible causes for hormonal problems and menstrual disorders. Hormonal fluctuations often play a central role, whether due to an overactive or underactive thyroid, an estrogen-progesterone imbalance, or stress, which can impair hormone production. Chronic conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis can also lead to cycle problems. Other factors such as nutritional deficiencies, excessive exercise, or the influence of medications should also be considered for an accurate diagnosis.
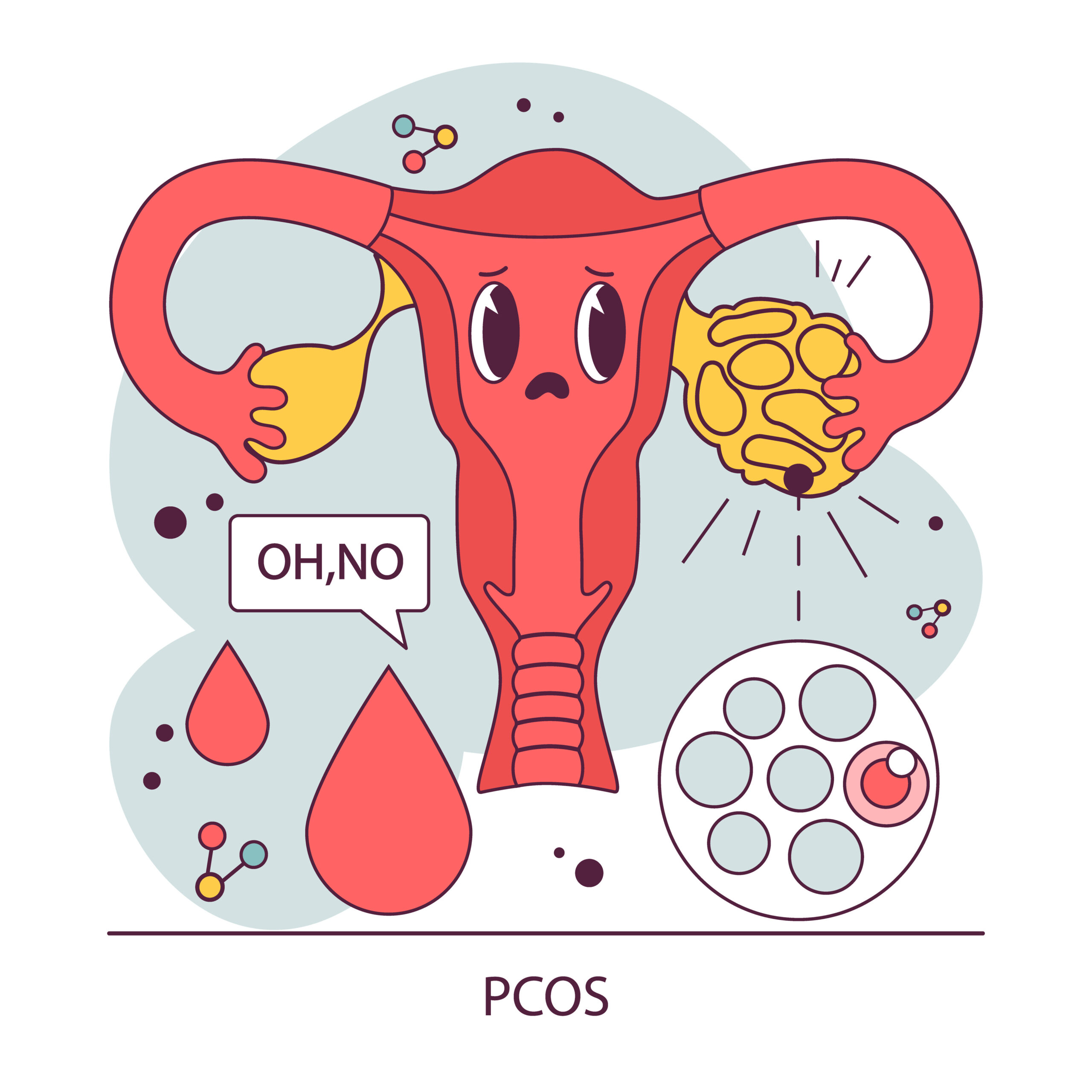
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS/PCO syndrome for short, is the most common metabolic disorder in sexually mature women, affecting 5-10% of women.
The exact cause of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is still unclear, but genetic factors and various mechanisms play a role. PCOS is characterized by a disturbed hormonal balance and impaired ovarian function. It is often associated with impaired insulin metabolism, which can trigger increased production of male hormones.
The consequences are often a disrupted menstrual cycle, infertility, increased body hair, hair loss, and obesity. Treatment includes medication, hormonal contraceptives, weight loss, and a modified diet. Comprehensive medical care is essential.
Next Steps
- Anamnesis: Recording of menstrual cycle, unfulfilled desire to have children (sterility), so-called androgenization signs, acne or hair loss) and weight development.
- Special ultrasound examination: Visualization of the ovaries using high-resolution transvaginal ultrasound, among other things to determine the presence of polycystic ovaries and as part of therapy follow-up.
- Physical examination / whole-body status / assessment of metabolic status
- Laboratory diagnostics: Special hormone analysis, thyroid and other metabolic parameters, lipid metabolism, and exclusion of insulin resistance.